Dockerise the Flask Webhook Receiver
We will now dockerise the Python Flask Webhook Receiver, that we built over the last two posts.
Our requirements are quite straight-forward:
- The docker image should be quite small, as we are not doing need anything fancy. Keeping it simple.
- No need to have external volume to backup our json file, as our app provides the ability to download(backup) the received notifications json file.
- If we make adjustments to the python file, we need to be able to easily re-build the docker image.
To follow along, the files are available here. Github
We will be paying close attention to the following files:
- Dockerfile - this is the file we will use to build our docker image. The focus here is what to package the image with.
- docker-compose.yml - this is the file we will use with docker-compose to define and run docker container.
Code Breakdown - Dockerfile
1
2
3
4
5
FROM python:slim
ADD . /python-flask
WORKDIR /python-flask
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
CMD [ "python3", "flask_rx_web_view.py"]
- Line 1 - python slim base image - docker build will use this create the image. More details below, as we explore which base image is the best to use - in terms of size and ease of use.
- Line 2 - we add all the files and folder into the image under a folder called “python-flask”.
- Line 3 - makes the working directory that folder so that when we use the “pip install” commands it will pick up the “requirements.txt” file.
- Line 4 - “pip install” install all the python3 required files to use the python code.
- Line 5 - This kicks off the self contained app = “python3 flask_rx_web_view.py”
To build the docker image from the Dockerfile. You must be in the same directory as Dockerfile file, before you can use the “docker build” command.
Directory structure used:
.
├── all_webhooks_detailed.json
├── config.py
├── Dockerfile
├── docker-compose.yml
├── flask_rx.py
├── flask_rx_web_view.py
├── requirements.txt
├── templates
│ └── bootstrap.html
├── test_webhook.py
└── userpass_base64.py
$ sudo docker build -t docker-webhook-slim:latest .
- docker-webhook-slim:latest this is where you specify the name of the image
- . the trailing period “ . “ is used to specified where it should look for the Dockerfile. The “ . “ means in current folder where the command was issued.
Tip:
Depending on your installation of docker, you may need the ‘sudo’ option in front of the docker command.
Which base image to use
The two criteria I had were:
- Ease of usage
- Disk size utilisation
To do test these, I change the first line in the Dockerfile, where it begins with “FROM” followed by one of the below listed candidates, one at a time:
- python:alpine
- python:slim
- python:3.9.1
and issue the respective docker build commands:
$ sudo docker build -t docker-webhook-alpine:latest .
$ sudo docker build -t docker-webhook-slim:latest .
$ sudo docker build -t docker-webhook:latest .
Ease of use
This is a simple test. To answer the following question: Can I use the base image from docker as is without having to compile extra bits and pieces?
During the docker build python:slim and python:3.9.1 passed - no issues encountered.
While testing with Alpine, it failed to pip install “cryptography”. Some python dependency are written in C and these needed to be compiled. Alpine based image has some of these “extra” things removed to make the base image size small. It is not worth the time to investigate and fix these issues.
Below is a snippet of the failed docker build, when trying to use the alpine based image:
$ sudo docker build -t docker-webhook-alpine:latest .
Sending build context to Docker daemon 29.7kB
Step 1/5 : FROM python:alpine
alpine: Pulling from library/python
540db60ca938: Pull complete
d037ddac5dde: Pull complete
629719f9106a: Pull complete
f9ef3a05a91e: Pull complete
0faf4e7f2207: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:02311d686cd35b0f838854d6035c679acde2767a4fd09904e65355fbd9780f8a
Status: Downloaded newer image for python:alpine
---> 2d64a2341b7c
Step 2/5 : ADD . /python-flask
---> 88e854b5f73d
Step 3/5 : WORKDIR /python-flask
---> Running in d5585bc21250
Removing intermediate container d5585bc21250
---> 2c6c04dd367c
Step 4/5 : RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
---> Running in 76cd242f3631
Collecting Flask==2.0.0
Downloading Flask-2.0.0-py3-none-any.whl (93 kB)
Collecting requests==2.24.0
Downloading requests-2.24.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (61 kB)
Collecting Flask_BasicAuth==0.2.0
Downloading Flask-BasicAuth-0.2.0.tar.gz (16 kB)
Collecting urllib3==1.25.11
Downloading urllib3-1.25.11-py2.py3-none-any.whl (127 kB)
Collecting cryptography==3.4.7
Downloading cryptography-3.4.7.tar.gz (546 kB)
Installing build dependencies: started
Installing build dependencies: finished with status 'error'
ERROR: Command errored out with exit status 1:
---- SNIPPET ----
WARNING: Discarding https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/9b/77/461087a514d2e8ece1c975d8216bc03f7048e6090c5166bc34115afdaa53/cryptography-3.4.7.tar.gz#sha256=3d10de8116d25649631977cb37da6cbdd2d6fa0e0281d014a5b7d337255ca713 (from https://pypi.org/simple/cryptography/) (requires-python:>=3.6). Command errored out with exit status 1: /usr/local/bin/python /tmp/pip-standalone-pip-43x5y3xp/__env_pip__.zip/pip install --ignore-installed --no-user --prefix /tmp/pip-build-env-amrtsd8g/overlay --no-warn-script-location --no-binary :none: --only-binary :none: -i https://pypi.org/simple -- 'setuptools>=40.6.0' wheel 'cffi>=1.12; platform_python_implementation != '"'"'PyPy'"'"'' 'setuptools-rust>=0.11.4' Check the logs for full command output.
ERROR: Could not find a version that satisfies the requirement cryptography==3.4.7 (from versions: 0.1, 0.2, 0.2.1, 0.2.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.5.1, 0.5.2, 0.5.3, 0.5.4, 0.6, 0.6.1, 0.7, 0.7.1, 0.7.2, 0.8, 0.8.1, 0.8.2, 0.9, 0.9.1, 0.9.2, 0.9.3, 1.0, 1.0.1, 1.0.2, 1.1, 1.1.1, 1.1.2, 1.2, 1.2.1, 1.2.2, 1.2.3, 1.3, 1.3.1, 1.3.2, 1.3.3, 1.3.4, 1.4, 1.5, 1.5.1, 1.5.2, 1.5.3, 1.6, 1.7, 1.7.1, 1.7.2, 1.8, 1.8.1, 1.8.2, 1.9, 2.0, 2.0.1, 2.0.2, 2.0.3, 2.1, 2.1.1, 2.1.2, 2.1.3, 2.1.4, 2.2, 2.2.1, 2.2.2, 2.3, 2.3.1, 2.4, 2.4.1, 2.4.2, 2.5, 2.6, 2.6.1, 2.7, 2.8, 2.9, 2.9.1, 2.9.2, 3.0, 3.1, 3.1.1, 3.2, 3.2.1, 3.3, 3.3.1, 3.3.2, 3.4, 3.4.1, 3.4.2, 3.4.3, 3.4.4, 3.4.5, 3.4.6, 3.4.7)
ERROR: No matching distribution found for cryptography==3.4.7
Output when building with the slim base image:
$ sudo docker build -t docker-webhook-slim:latest .
Sending build context to Docker daemon 28.67kB
Step 1/5 : FROM python:slim
slim: Pulling from library/python
69692152171a: Pull complete
59773387c0e7: Pull complete
3fc84e535e87: Pull complete
68ebeebdab6f: Pull complete
3d3af2ef8baa: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:80b238ba357d98813bcc425f505dfa238f49cf5f895492fc2667af118dccaa44
Status: Downloaded newer image for python:slim
---> 609da079b03a
Step 2/5 : ADD . /python-flask
---> 9d6141a8090b
Step 3/5 : WORKDIR /python-flask
---> Running in a22811e15ce3
Removing intermediate container a22811e15ce3
---> b144dc73d1e7
Step 4/5 : RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
---> Running in 32a14664de06
Collecting Flask==2.0.0
Downloading Flask-2.0.0-py3-none-any.whl (93 kB)
Collecting requests==2.24.0
Downloading requests-2.24.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (61 kB)
Collecting Flask_BasicAuth==0.2.0
Downloading Flask-BasicAuth-0.2.0.tar.gz (16 kB)
Collecting urllib3==1.25.11
Downloading urllib3-1.25.11-py2.py3-none-any.whl (127 kB)
Collecting cryptography==3.4.7
Downloading cryptography-3.4.7-cp36-abi3-manylinux2014_x86_64.whl (3.2 MB)
Collecting click>=7.1.2
Downloading click-8.0.1-py3-none-any.whl (97 kB)
Collecting Jinja2>=3.0
Downloading Jinja2-3.0.1-py3-none-any.whl (133 kB)
Collecting Werkzeug>=2.0
Downloading Werkzeug-2.0.1-py3-none-any.whl (288 kB)
Collecting itsdangerous>=2.0
Downloading itsdangerous-2.0.1-py3-none-any.whl (18 kB)
Collecting idna<3,>=2.5
Downloading idna-2.10-py2.py3-none-any.whl (58 kB)
Collecting chardet<4,>=3.0.2
Downloading chardet-3.0.4-py2.py3-none-any.whl (133 kB)
Collecting certifi>=2017.4.17
Downloading certifi-2021.5.30-py2.py3-none-any.whl (145 kB)
Collecting cffi>=1.12
Downloading cffi-1.14.5-cp39-cp39-manylinux1_x86_64.whl (406 kB)
Collecting pycparser
Downloading pycparser-2.20-py2.py3-none-any.whl (112 kB)
Collecting MarkupSafe>=2.0
Downloading MarkupSafe-2.0.1-cp39-cp39-manylinux2010_x86_64.whl (30 kB)
Building wheels for collected packages: Flask-BasicAuth
Building wheel for Flask-BasicAuth (setup.py): started
Building wheel for Flask-BasicAuth (setup.py): finished with status 'done'
Created wheel for Flask-BasicAuth: filename=Flask_BasicAuth-0.2.0-py3-none-any.whl size=4243 sha256=b1b3cfae942ef1cde32244fa52fd862aa2856742a8f843937035871df2cafe85
Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/d4/5a/db/e442580c22be34f69e537448832d7e1ee5a9c5adb63ace30bf
Successfully built Flask-BasicAuth
Installing collected packages: MarkupSafe, Werkzeug, pycparser, Jinja2, itsdangerous, click, urllib3, idna, Flask, chardet, cffi, certifi, requests, Flask-BasicAuth, cryptography
Successfully installed Flask-2.0.0 Flask-BasicAuth-0.2.0 Jinja2-3.0.1 MarkupSafe-2.0.1 Werkzeug-2.0.1 certifi-2021.5.30 cffi-1.14.5 chardet-3.0.4 click-8.0.1 cryptography-3.4.7 idna-2.10 itsdangerous-2.0.1 pycparser-2.20 requests-2.24.0 urllib3-1.25.11
WARNING: Running pip as root will break packages and permissions. You should install packages reliably by using venv: https://pip.pypa.io/warnings/venv
Removing intermediate container 32a14664de06
---> 2ec9070f8878
Step 5/5 : CMD [ "python3", "flask_rx_web_view.py"]
---> Running in cfcd90b43557
Removing intermediate container cfcd90b43557
---> b3e8c958a052
Successfully built b3e8c958a052
Successfully tagged docker-webhook-slim:latest
Based on these test, I am NOT going to use the Alpine based image, as it will need more work to make it usable.
Disk size
By changing the first line in Dockerfile, we can test which based image we will use based on size. Here are the resulting images and their sizes from the Ubuntu VM. Raw output
$ sudo docker image ls
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
<none> <none> 2c6c04dd367c 50 minutes ago 45.1MB
docker-webhook-slim latest b3e8c958a052 20 hours ago 147MB
docker-webhook latest ab7a0c5cc41c 3 days ago 917MB
python alpine 2d64a2341b7c 2 weeks ago 45MB
python slim 609da079b03a 2 weeks ago 115MB
python 3.9.1 2a93c239d591 4 months ago 885MB
Interpretation of the data
Base image + our python-flask-webhook - LINUX/AMD64
| “FROM” value | image name:tag | Description | Uncompressed Size | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| python:alpine | N/A | python-flask-webhook + Base alpine | N/A | Failed to build |
| python:slim | docker-webhook-slim:latest | python-flask-webhook + Base slim | 147MB | Base image + our app |
| python:3.9.1 | docker-webhook:latest | python-flask-webhook + Base 3.9.1 | 917MB | Base image + our app |
Base image only - LINUX/AMD64
| Base Image | Description | Uncompressed Size | Compressed Size* |
|---|---|---|---|
| python:alpine | python base image only - alpine | 45MB | 16.43 MB |
| python:slim | python base image only - slim | 115MB | 41.47 MB |
| python:3.9.1 | python base image only - 3.9.1 | 885MB | 324.08 MB |
Compressed Size* from Docker hub.
Looks like our Flask Webhook receiver app adds about 32 MB on top of the Base image size. Using Python Slim is an easy choice - it is 6 times smaller than python:3.9.1 and it passed the “Ease of use” test.
The full list of docker python base images are available from Docker Official Images
Start our first container
Let’s start the slim based image.
sudo docker run --name Webhook-App -p 5443:5443 docker-webhook-slim:latest
- —name Webhook-App this is the name of the container.
- -p 5443:5443 this is mapping the port from the container to the host.
- docker-webhook-slim:latest this is the image we should use to start this container.
$ sudo docker run --name Webhook-App -p 5443:5443 docker-webhook-slim:latest
* Serving Flask app 'flask_rx_web_view' (lazy loading)
* Environment: production
WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment.
Use a production WSGI server instead.
* Debug mode: on
* Running on all addresses.
WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment.
* Running on https://172.17.0.2:5443/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
* Restarting with stat
* Debugger is active!
* Debugger PIN: 103-683-561
10.66.254.32 - - [14/Jun/2021 08:01:37] "GET /log HTTP/1.1" 200 -
10.66.254.32 - - [14/Jun/2021 08:01:48] "GET /log HTTP/1.1" 200 -
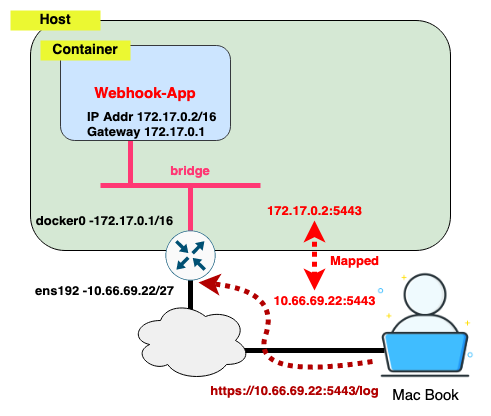
Note that it show its IP address is 172.17.0.2. This is the IP address that Docker bridge assigned to it. Also TCP port 5443 from 172.17.0.2 is mapped to the host TCP port 5443. To investigate further:
$ sudo docker inspect Webhook-App | grep -A 50 NetworkSetting
"NetworkSettings": {
"Bridge": "",
"SandboxID": "0a94e1cbe66a30b4accd60d9f5a171c9accc72fbb31ab1d394dafa20e4bcdcef",
"HairpinMode": false,
"LinkLocalIPv6Address": "",
"LinkLocalIPv6PrefixLen": 0,
"Ports": {
"5443/tcp": [
{
"HostIp": "0.0.0.0",
"HostPort": "5443"
}
]
},
"SandboxKey": "/var/run/docker/netns/0a94e1cbe66a",
"SecondaryIPAddresses": null,
"SecondaryIPv6Addresses": null,
"EndpointID": "771925244b4ebf81cca2f5f44e8849cb5eaba177f92f38d22900846c0a5494a1",
"Gateway": "172.17.0.1",
"GlobalIPv6Address": "",
"GlobalIPv6PrefixLen": 0,
"IPAddress": "172.17.0.2",
"IPPrefixLen": 16,
"IPv6Gateway": "",
"MacAddress": "02:42:ac:11:00:02",
"Networks": {
"bridge": {
"IPAMConfig": null,
"Links": null,
"Aliases": null,
"NetworkID": "4553eecb43bc8e8457ecc6f79c71ead180e104b24cdea3c7f8e60ec6efc200b3",
"EndpointID": "771925244b4ebf81cca2f5f44e8849cb5eaba177f92f38d22900846c0a5494a1",
"Gateway": "172.17.0.1",
"IPAddress": "172.17.0.2",
"IPPrefixLen": 16,
"IPv6Gateway": "",
"GlobalIPv6Address": "",
"GlobalIPv6PrefixLen": 0,
"MacAddress": "02:42:ac:11:00:02",
"DriverOpts": null
}
}
}
}
]
Tip:
Previous “docker run” leaves you attached to the container. To run the container detached or headless mode use the “-d” option.
Otherwise Ctrl-C will kill your container, and you will have to restart it with:
$ sudo docker restart Webhook-App
To use “docker run” with detach ‘-d’ option.
sudo docker run --name Webhook-App -d -p 5443:5443 docker-webhook-slim:latest
List of useful commands:
To check the status of a running container.
$ sudo docker container ls -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
4d2066336f57 docker-webhook-slim:latest "python3 flask_rx_we…" 5 hours ago Up 2 hours 0.0.0.0:5443->5443/tcp Webhook-App
Stop a running container.
$ sudo docker container stop Webhook-App
Webhook-App
$
Delete the container.
$ sudo docker container rm Webhook-App
Webhook-App
$
Next Level It! Docker-compose
Docker-compose is taking those simple docker commands we saw above to the next level. With one yml file (docker-compose.yml), you can build and launch more than containers at the same time. What I find appealing is that it can be used in development environment when your python code keeps changing, and you are sick of going through the process of stop/remove containers, and re-build new image. Then start the containers up again.
Code Breakdown - docker-compose.yml
The content of docker-compose.yml
1
2
3
4
5
6
version: "3.8"
services:
app:
build: .
ports:
- "5443:5443"
- build - specify the location of Dockerfile
- ports - help map out the TCP port mapping - usually done with “docker build …”
- version - is to tell docker-compose, what format the yml file was written for,
To kick it off - make sure this command issue in the same folder as where docker-compose.yml, Dockerfile, and where all the other files are.
Notice:
It created a new network called “webhook_default”, and with a new IP address range - 172.18.0.2
$ sudo docker-compose up
Creating network "webhook_default" with the default driver
Building app
Sending build context to Docker daemon 29.7kB
Step 1/5 : FROM python:slim
---> 609da079b03a
Step 2/5 : ADD . /python-flask
---> 05eb1e22a811
Step 3/5 : WORKDIR /python-flask
---> Running in 8e3406cdda68
Removing intermediate container 8e3406cdda68
---> 8271ad0c7025
Step 4/5 : RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
---> Running in 96beb163dc0d
Collecting Flask==2.0.0
Downloading Flask-2.0.0-py3-none-any.whl (93 kB)
Collecting requests==2.24.0
Downloading requests-2.24.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (61 kB)
Collecting Flask_BasicAuth==0.2.0
Downloading Flask-BasicAuth-0.2.0.tar.gz (16 kB)
Collecting urllib3==1.25.11
Downloading urllib3-1.25.11-py2.py3-none-any.whl (127 kB)
Collecting cryptography==3.4.7
Downloading cryptography-3.4.7-cp36-abi3-manylinux2014_x86_64.whl (3.2 MB)
Collecting Werkzeug>=2.0
Downloading Werkzeug-2.0.1-py3-none-any.whl (288 kB)
Collecting itsdangerous>=2.0
Downloading itsdangerous-2.0.1-py3-none-any.whl (18 kB)
Collecting Jinja2>=3.0
Downloading Jinja2-3.0.1-py3-none-any.whl (133 kB)
Collecting click>=7.1.2
Downloading click-8.0.1-py3-none-any.whl (97 kB)
Collecting certifi>=2017.4.17
Downloading certifi-2021.5.30-py2.py3-none-any.whl (145 kB)
Collecting idna<3,>=2.5
Downloading idna-2.10-py2.py3-none-any.whl (58 kB)
Collecting chardet<4,>=3.0.2
Downloading chardet-3.0.4-py2.py3-none-any.whl (133 kB)
Collecting cffi>=1.12
Downloading cffi-1.14.5-cp39-cp39-manylinux1_x86_64.whl (406 kB)
Collecting pycparser
Downloading pycparser-2.20-py2.py3-none-any.whl (112 kB)
Collecting MarkupSafe>=2.0
Downloading MarkupSafe-2.0.1-cp39-cp39-manylinux2010_x86_64.whl (30 kB)
Building wheels for collected packages: Flask-BasicAuth
Building wheel for Flask-BasicAuth (setup.py): started
Building wheel for Flask-BasicAuth (setup.py): finished with status 'done'
Created wheel for Flask-BasicAuth: filename=Flask_BasicAuth-0.2.0-py3-none-any.whl size=4243 sha256=08c6a441f639c97b7a16d813aaf253eec4536a46a915d6dab63d1fac6173c9fb
Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/d4/5a/db/e442580c22be34f69e537448832d7e1ee5a9c5adb63ace30bf
Successfully built Flask-BasicAuth
Installing collected packages: MarkupSafe, Werkzeug, pycparser, Jinja2, itsdangerous, click, urllib3, idna, Flask, chardet, cffi, certifi, requests, Flask-BasicAuth, cryptography
Successfully installed Flask-2.0.0 Flask-BasicAuth-0.2.0 Jinja2-3.0.1 MarkupSafe-2.0.1 Werkzeug-2.0.1 certifi-2021.5.30 cffi-1.14.5 chardet-3.0.4 click-8.0.1 cryptography-3.4.7 idna-2.10 itsdangerous-2.0.1 pycparser-2.20 requests-2.24.0 urllib3-1.25.11
WARNING: Running pip as root will break packages and permissions. You should install packages reliably by using venv: https://pip.pypa.io/warnings/venv
Removing intermediate container 96beb163dc0d
---> 9b92aced761a
Step 5/5 : CMD [ "python3", "flask_rx_web_view.py"]
---> Running in d7a262c4fdba
Removing intermediate container d7a262c4fdba
---> 476ebe2098e9
Successfully built 476ebe2098e9
Successfully tagged webhook_app:latest
WARNING: Image for service app was built because it did not already exist. To rebuild this image you must use `docker-compose build` or `docker-compose up --build`.
Creating webhook_app_1 ... done
Attaching to webhook_app_1
app_1 | * Serving Flask app 'flask_rx_web_view' (lazy loading)
app_1 | * Environment: production
app_1 | WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment.
app_1 | Use a production WSGI server instead.
app_1 | * Debug mode: on
app_1 | * Running on all addresses.
app_1 | WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment.
app_1 | * Running on https://172.18.0.2:5443/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
app_1 | * Restarting with stat
app_1 | * Debugger is active!
app_1 | * Debugger PIN: 991-656-352
app_1 | 10.66.255.106 - - [14/Jun/2021 13:19:13] "GET /log HTTP/1.1" 200 -
app_1 | 10.66.255.106 - - [14/Jun/2021 13:19:16] "GET /log HTTP/1.1" 200 -
^CGracefully stopping... (press Ctrl+C again to force)
Stopping webhook_app_1 ... done
In one command, it built the image and started the container.
$ sudo docker image ls
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
webhook_app latest db6bc5a66104 47 seconds ago 147MB
python slim 609da079b03a 2 weeks ago 115MB
python 3.9.1 2a93c239d591 4 months ago 885MB
$ sudo docker container ls
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
8581b534183f webhook_app "python3 flask_rx_we…" About a minute ago Up About a minute 0.0.0.0:5443->5443/tcp webhook_app_1
c
With one command, we can stop and delete the container. The only thing left is the image.
$ sudo docker-compose down
Stopping webhook_app_1 ... done
Removing webhook_app_1 ... done
Removing network webhook_default
$
$ sudo docker image ls
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
webhook_app latest db6bc5a66104 3 minutes ago 147MB
python slim 609da079b03a 2 weeks ago 115MB
python 3.9.1 2a93c239d591 4 months ago 885MB
$ sudo docker container ls -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
$
If you make changes to the python code or anything within the folder, and we want to update the docker image with the changes. All you have to do is “docker-compose up –build”. And it will rebuild the image, and start the container again. So cool !
$ sudo docker-compose up --build -d
Creating network "webhook_default" with the default driver
Building app
Sending build context to Docker daemon 29.7kB
Step 1/5 : FROM python:slim
---> 609da079b03a
Step 2/5 : ADD . /python-flask
---> 988150493dc7
Step 3/5 : WORKDIR /python-flask
---> Running in 1a42c4998dd5
Removing intermediate container 1a42c4998dd5
---> 2abc1516ffd1
Step 4/5 : RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
---> Running in 6a2f3daac6f8
Collecting Flask==2.0.0
Downloading Flask-2.0.0-py3-none-any.whl (93 kB)
Collecting requests==2.24.0
Downloading requests-2.24.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (61 kB)
Collecting Flask_BasicAuth==0.2.0
Downloading Flask-BasicAuth-0.2.0.tar.gz (16 kB)
Collecting urllib3==1.25.11
Downloading urllib3-1.25.11-py2.py3-none-any.whl (127 kB)
Collecting cryptography==3.4.7
Downloading cryptography-3.4.7-cp36-abi3-manylinux2014_x86_64.whl (3.2 MB)
Collecting itsdangerous>=2.0
Downloading itsdangerous-2.0.1-py3-none-any.whl (18 kB)
Collecting Jinja2>=3.0
Downloading Jinja2-3.0.1-py3-none-any.whl (133 kB)
Collecting click>=7.1.2
Downloading click-8.0.1-py3-none-any.whl (97 kB)
Collecting Werkzeug>=2.0
Downloading Werkzeug-2.0.1-py3-none-any.whl (288 kB)
Collecting idna<3,>=2.5
Downloading idna-2.10-py2.py3-none-any.whl (58 kB)
Collecting chardet<4,>=3.0.2
Downloading chardet-3.0.4-py2.py3-none-any.whl (133 kB)
Collecting certifi>=2017.4.17
Downloading certifi-2021.5.30-py2.py3-none-any.whl (145 kB)
Collecting cffi>=1.12
Downloading cffi-1.14.5-cp39-cp39-manylinux1_x86_64.whl (406 kB)
Collecting pycparser
Downloading pycparser-2.20-py2.py3-none-any.whl (112 kB)
Collecting MarkupSafe>=2.0
Downloading MarkupSafe-2.0.1-cp39-cp39-manylinux2010_x86_64.whl (30 kB)
Building wheels for collected packages: Flask-BasicAuth
Building wheel for Flask-BasicAuth (setup.py): started
Building wheel for Flask-BasicAuth (setup.py): finished with status 'done'
Created wheel for Flask-BasicAuth: filename=Flask_BasicAuth-0.2.0-py3-none-any.whl size=4243 sha256=ecbaffc1216d42446ced99eb9f7d9aaef2b9b431bb3cd0d183bb3f741f878ff7
Stored in directory: /root/.cache/pip/wheels/d4/5a/db/e442580c22be34f69e537448832d7e1ee5a9c5adb63ace30bf
Successfully built Flask-BasicAuth
Installing collected packages: MarkupSafe, Werkzeug, pycparser, Jinja2, itsdangerous, click, urllib3, idna, Flask, chardet, cffi, certifi, requests, Flask-BasicAuth, cryptography
WARNING: Running pip as root will break packages and permissions. You should install packages reliably by using venv: https://pip.pypa.io/warnings/venv
Successfully installed Flask-2.0.0 Flask-BasicAuth-0.2.0 Jinja2-3.0.1 MarkupSafe-2.0.1 Werkzeug-2.0.1 certifi-2021.5.30 cffi-1.14.5 chardet-3.0.4 click-8.0.1 cryptography-3.4.7 idna-2.10 itsdangerous-2.0.1 pycparser-2.20 requests-2.24.0 urllib3-1.25.11
Removing intermediate container 6a2f3daac6f8
---> 2afd1950c646
Step 5/5 : CMD [ "python3", "flask_rx_web_view.py"]
---> Running in a82ef81142da
Removing intermediate container a82ef81142da
---> e34029941778
Successfully built e34029941778
Successfully tagged webhook_app:latest
Creating webhook_app_1 ... done
$ sudo docker image ls
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
webhook_app latest e34029941778 About a minute ago 147MB
<none> <none> db6bc5a66104 8 minutes ago 147MB
python slim 609da079b03a 2 weeks ago 115MB
python 3.9.1 2a93c239d591 4 months ago 885MB
Notice it left the previous built image behind (IMAGE ID = db6bc5a66104” - see above). No big deal - easily cleaned up manually with the “docker image rm db6bc5a66104” where db6bc5a66104 is the IMAGE ID.
Summary
We have come along way from 2 posts ago. We were talking about webhooks, python and the power of flask. As well as discussing bootstrapping HTML code. To now, where we have taken all that and turn it into a functioning docker application. Which we can spin up and down easily.
Hopefully, you have found it useful.
As always, please reach out if you have any questions or comments or suggestions.